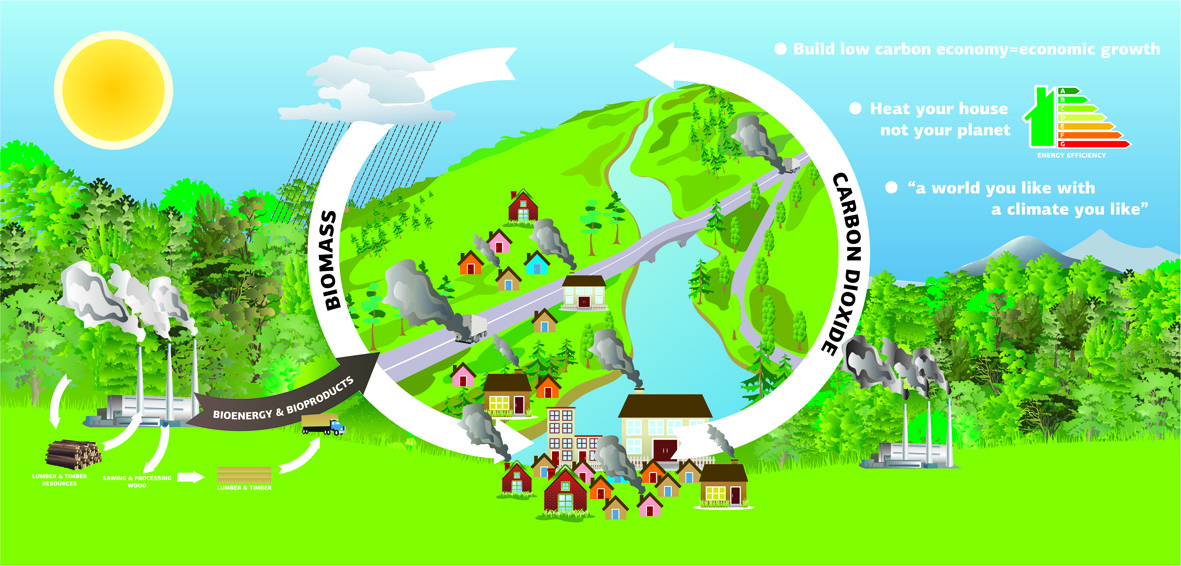
What is biomass?
Biomass is any organic substance (solid or liquid) which comes from agriculture, forestry (and related sectors) or any other industrial and household waste which can be used for the production of energy / heat. This means that this alternative source of energy is more economical from the conventional sources of liquid fuel (such as diesel, mazout, probane, electricity) and most important the utilization of biomass causes less impact on the green house gas, contributing this way to a greener planet.
The main sources of biomass come from:
- Wood / Forestry:
Forestry and the related sectors of wood products (carpentries, panel and floor producers etc) are the main source of biomass in this sector. The sector covers a wide range of products (such as logs, sawdust and carpentry wastages)-and has also offered the wood-briquettes and most recently the wood pellets. The wood briquettes and the wood pellets have high density and very high calorific value therefore they can greatly contribute in the development of bio-energy world-wide.
- Agriculture and animal feeding:
Various plants can be cultivated and processed to produce bio-diesel. The most popular plants are corn-oil, sunflower etc. In the last couple of years the extensive usage of these plants have caused tremendous increases on the basic prices of the food (wheat and corn) as the demand of the bio-diesel is huge and the available land decreases. . Farm waste can also be processed for the production of energy / heat locally thus decreasing their energy cost.
- Bio-Processed water /sewage’s:
The bio-processed water includes many types of waste such as organic public and household (solid or liquid). Every form of biomass has many characteristics including humidity, calorific value and ash. Therefore a different way of processing of bio-energy production is required for every sewage item. This processing / transformation requires chemical and biological treatment which can be covered by independent units or local network.
Biomass Utilization:
- Biomass for Heat Production
The combustion of solid pieces (mainly wood) for heat production is the main source of bio-energy heat with the continuous increase of efficiency and decrease of emissions. The various systems for heat production correspond to the space and the temperature which are set to perform. Smaller household units utilize firewood, briquette, pellet in stoves and burners. Larger size systems can operate with various biomass fuels: eg wood, corn sunflower pellet for various industrial usages such as farms, hospitals, houses etc). In even larger systems there may be co-production of heat and steam for the local plant network.
- Biomass for Electricity Production
The production of electricity arises from a combined cycle of heat and steam. The biomass is the main source of combustion but it can be enriched with coal for increased performance. The bio-gas is still a way for energy production with the utilization of methanion from the composition of wastages and which can then be injected into the gas chamber.
- Biodiesel
Biodiesel Various forms of liquid gas and fuel which are produced from vegetarian and cooking oils are processed and used for transportation. Depending on their composition the vehicle equipment may need to be modified or even replaced. At the moment there is a great research undergoing for the utilization of oils and paints which will be beneficial and reduce transportation costs.
Advantages on the Usage of Biomass:
- Lower cost and immediate availability in Cyprus (on some items) and in nearby countries therefore its import is relative easy and quick.
- It aids the reduction of the independence on the traditional sources of energy such as oil, gas which are exclusive by imports.
- It contributes to the creation of the energy balance in the local economy and is less vulnerable to price changes.
- It can be easily stored when needed without big costs on storage facilities.
- It is an ecological product, its usage is less harmful on the environment and contributes to the reduction of the green house effect.
- The recycling and saving of the natural resources creates green ecomomic development and in the wider society.
- It offers many new job positions in sectors which are enjoying substantial economic growth and technology.
- The utilization of forest in the biomass production, where there is a manageable forest sustainable program, contributes to the reduction of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere rather than the utilization of the conventional liquid fuels. The latter is responsible for the increase of the planet temperature with all the climate change implications.

